
Fuel transformation has become a major trend in the global shipping industry. In the first five months of this year, global green ship orders continued to grow, with a cumulative amount of up to 250 billion yuan. In this green wave, Chinese shipbuilders, with absolute strength, are "far ahead" and firmly hold the leading position.
According to the latest statistics from Clarkson, among the total 541 new ship orders of 34.6 million gross tons worldwide from January to May this year, as many as 273 ships of 16 million gross tons are alternative fuel ships, accounting for 46.2%, exceeding 40.6% of the whole of last year, but lower than the historical record of 54.3% for the whole of 2022. Calculated by order value, the total global new shipbuilding investment from January to May was 69.2 billion US dollars, and the order value of alternative fuel ships was 34.2 billion US dollars (approximately 248.326 billion yuan), increasing by 29% year-on-year, accounting for 49.4%.
This year's alternative fuel ship orders include 97 LNG-powered ships of 10.7 million gross tons, 38 methanol-powered ships of 2.4 million gross tons, 44 LPG-powered ships of 1.8 million gross tons, and 85 battery/hybrid propulsion ships of 0.7 million gross tons.
In recent years, the proportion of alternative fuel ships in new ship orders has been climbing all the way, rising from only 8.2% in 2016 to 32% in 2021, and reaching the highest in history of 54% in 2022, with only a slight decline last year.
According to statistics, among the total 2,071 new ship orders of 85.8 million gross tons throughout 2023, 575 ships of 34.9 million gross tons are alternative fuel ships. Among them, there are 219 LNG-powered ships of 19.2 million gross tons, accounting for about 22% of the total order volume; 135 methanol-powered ships of 10.7 million gross tons, accounting for about 12% of the total order volume; 48 LPG-powered ships, and 147 battery/hybrid propulsion ships.
In terms of shipyards by country, Clarkson's data shows that the vast majority of alternative fuel new ship orders in May 2024 were taken by Chinese shipyards, totaling up to 29 ships of 834,000 CGT, accounting for 79% of the alternative fuel new ship orders in May 2024 by CGT, far ahead of other competitors. In contrast, South Korean shipyards undertook 2 new ship orders of 170,000 CGT of alternative fuels in May, with a market share of 16%.
Among the 29 alternative fuel new ship orders of 834,000 CGT undertaken by Chinese shipyards in May 2024, there are 10 LNG dual-fuel ships of 403,000 CGT, 9 methanol dual-fuel ships of 227,000 CGT, 4 LPG dual-fuel ships of 113,000 CGT, 2 ammonia dual-fuel ships of 31,000 CGT, and 4 battery/hybrid propulsion ships of 61,000 CGT. The 2 alternative fuel new ship orders of 170,000 CGT undertaken by South Korean shipyards are all LNG dual-fuel ships.
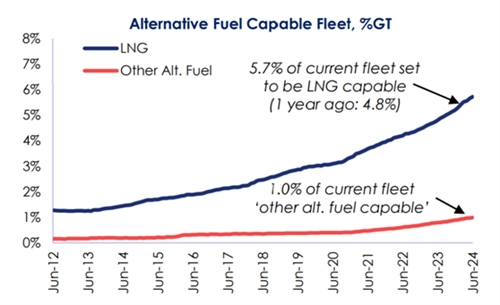
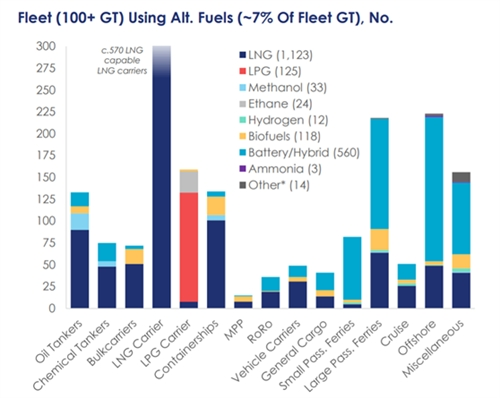
According to Clarkson's data, overall, by tonnage, the proportion of ships in the operating fleet that can use alternative fuels or propulsion devices has increased to 6.7% up to now, higher than 2.4% in 2017 and 4.6% at the beginning of 2022. Among the existing total of 1,890 alternative fuel ships, there are 1,123 LNG-powered ships, 33 methanol-powered ships, 125 LPG-powered ships, 559 battery/hybrid propulsion ships, and 167 ships using other fuels.
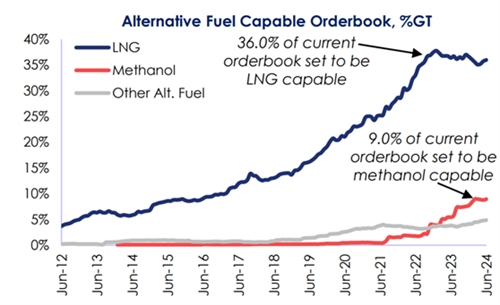
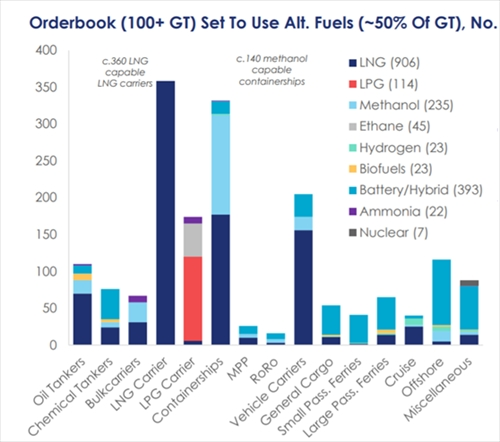
In the orderbook of ships on hand, the proportion of alternative fuel ships has reached 49.8%, higher than 10.7% in 2017 and 34.0% at the beginning of 2022. Calculated by tonnage, 36.0% of the orderbook is LNG-powered ships (906 ships), 9.0% is methanol-powered ships (235 ships), and 2.1% is LPG-powered ships (114 ships); in addition, approximately 2.8% (about 407 ships) use other alternative fuels, including 23 hydrogen fuel ships, 45 ethane fuel ships, 22 ammonia fuel ships, 23 biofuel ships, and 393 battery/hybrid propulsion ships. The total orderbook of alternative fuel ships amounts to 1,542 ships.
With the continuous expansion of future fuel options, the number of alternative fuel reserved ships is also increasing. Currently, there are 493 LNG-ready ships in the operating fleet, and there are still 144 in the orderbook. Meanwhile, there are 273 ammonia-ready ships, 343 methanol-ready ships, and 13 hydrogen-ready ships in the orderbook.
At the same time, the latest statistics from DNV's Alternative Fuels Insight (AFI) data platform indicate that there were a total of 33 alternative fuel ship orders in May this year, including 23 methanol fuel ships, 2 ammonia fuel ships, and 8 LNG-powered ships. Among the 23 methanol fuel ships, there are 10 container ships, as well as 5 bulk carriers and 4 car carriers.
DNV stated that the strong growth in May confirms the overall trend of a steady increase in new ship orders for alternative fuels. From January to May 2024, new ship orders for alternative fuel ships have reached 127, an increase of 55% year-on-year.
Jason Stefanatos, DNV's Global Decarbonization Director, said: "The demand for alternative fuel ships in the new ship order market is strong, and the data for May also confirms this. Methanol fuel dominates new ship orders. As of 2024, there have been 70 new orders for methanol-fueled ships, accounting for 55% of the total number of alternative fuel ship orders in 2024. Although, on the whole, the order volume of methanol fuel ships is still far behind LNG-powered ships, these latest data indicate a significant increase in market demand for methanol fuel ships. Ammonia fuel ships have also received two new orders, bringing the total number of orders this year to 11, compared with only two for the entire year of 2023. Although ammonia fuel ships are clearly still in the early stages, this further proves the rise of ammonia fuel in the alternative fuel market."

